Unit 1: Basic Economic Concepts
| Created | |
|---|---|
| Tags | In Class |
The basic principle of economics is that we have unlimited wants & needs, but a limited supply of resources. This concept is known as scarcity.
What is Economics?
- Economics is the science of scarcity.
- Scarcity means that we have unlimited wants but limited resources.
- Since we are unable to have everything we desire, we must make choices on how we will use our resources.
- Economics is the study of these choices.
- In Microeconomics, we will primarily study the choices of individuals and firms.
- Study of small economic markets such as individuals, firms, and industries (ex: supply and demand in specific markets, production costs, labor markets, etc.)
How is Economics used?
- Economists use the scientific method to make generalizations and abstractions to develop theories. This is called theoretical economics.
- These theories are then applied to fix problems or meet economic goals. This is called policy economics.
Positive vs. Normative
- Positive Statements: Basted on facts. Avoids value judgements (what is).
- Normative Statements: Includes value judgements (what ought to be).
5 Key Economic Assumptions
- Society's wants are unlimited, but ALL resources are limited (scarcity).
- Due to scarcity, choices must be made. Every choice has a cost (a trade-off).
- Everyone's goal is to maximize their satisfaction. Everyone acts in their own "self-interest."
- Everyone makes decisions by comparing the marginal costs and marginal benefits of every choice.
- Real-life situations can be modeled through simple graphs.
Marginal Analysis
- The term marginal means additional, or one more.
- "Thinking on the margin," or marginal analysis involves making decisions based on the additional benefit vs. the additional cost.
- The marginal analysis approach to decision making is more commonly used than the "all or nothing" approach.
- You will continue to do something until the marginal cost outweighs the marginal benefit.
Trade-offs and Opportunity Cost
- Trade-offs are all the alternatives that we give up whenever we choose one course of action over others.
- The most desirable alternative given up as a result of a decision is known as the opportunity cost.
The Four Factors of Production
- Land
- Labor
- Capital
- Entrepreneurship
These four factors of production are all SCARCE resources.
Economic Systems
An economic system is an organized method to provide for the wants & needs of a society.
Every economic system must answer three basic economic questions:
- What to produce?
- How to produce?
- For whom to produce?
The Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)
- An economic model for explaining the concept of opportunity cost
- A production possibilities curve is a model that shows alternative ways that an economy can use its scarce resources.
- This model graphically demonstrates scarcity, trade-offs, opportunity costs, and efficiency.
4 Key Assumptions
- Only two goods can be produced
- Full employment of resources
- Fixed Resources
- Fixed Technology
Any point which lies on the graph is the most efficient, while any point inside the curve does not make the most efficient use of all available resources.
Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost
- As you produce more of any good, the opportunity cost will increase
- Resources are NOT easily adaptable to producing both goods
- Result is a bowed out (Concave) PPC
Per Unit Opportunity Cost
Two Types of Efficiency
Productive Efficiency
- Products are being produced in the least costly way
- This is any point ON the PPC
Allocative Efficiency
- The products being produced are the ones most desired by society
- The optimal point on the PPC depends on the desires of society
Shifting the PPC
- Change in resource quantity or quality
- Technology improves
- More education or training
Comparative Advantage
While the absolute advantage merely compares the efficiency of production, comparative advantage compares the opportunity costs of production.
Output Method
OOO - Output: Other goes Over
Input Method
IOU - Input: Other goes Under
Marginal Utility & Marginal Cost
The formula to find utility maximization is:
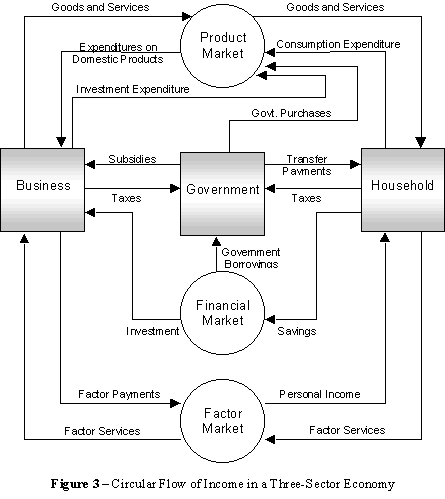
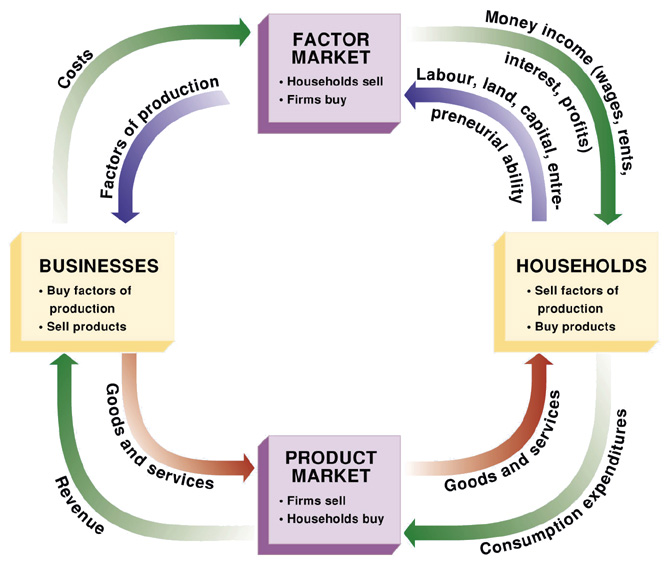
Factor & Product Markets
Factor Market
- Factors of production ⇒ money
- Households sell
- Firms buy
Product Market
- Money ⇒ Products / Goods and Services
- Firms sell
- Households buy
Government Involvement
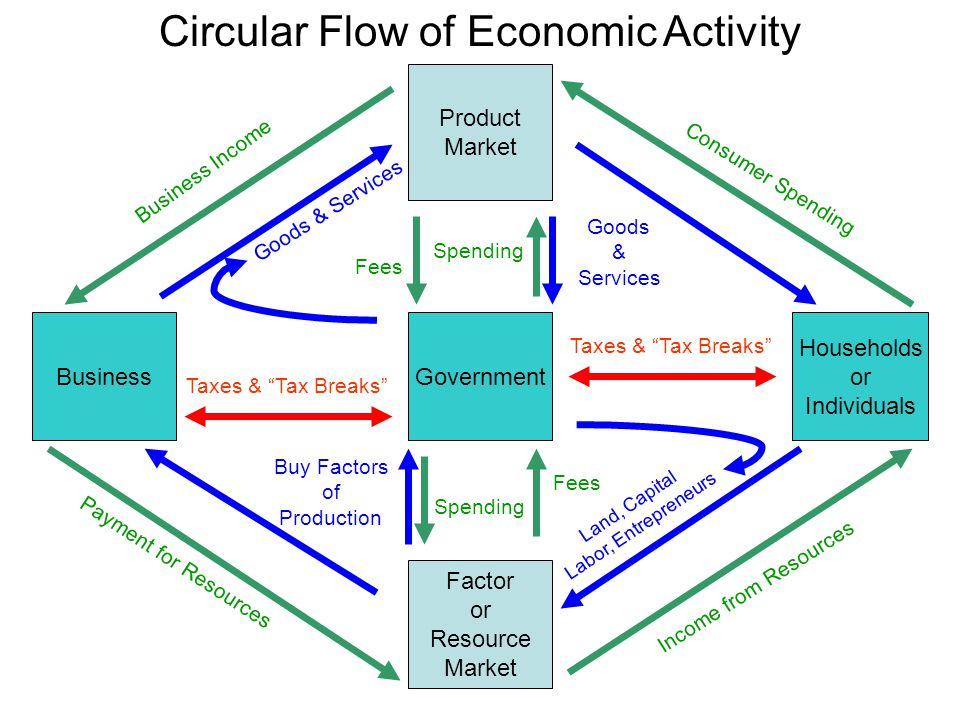
The government in a mixed-market economy acts as an intermediary between many aspects of the Factor and Product markets.
Financial Institutions & Government